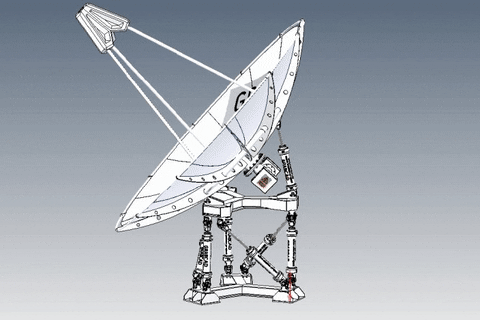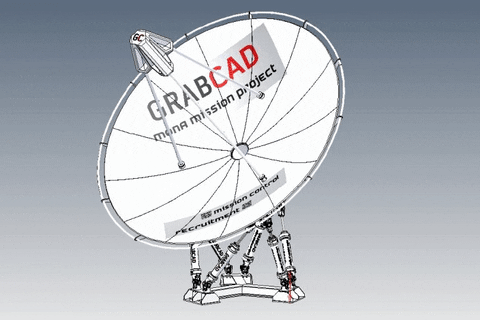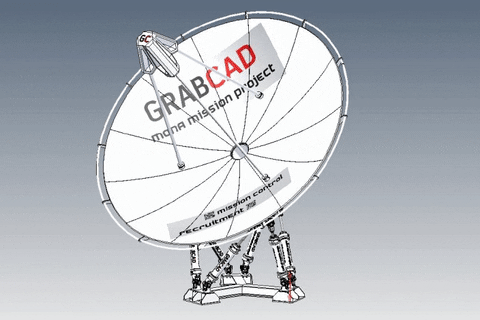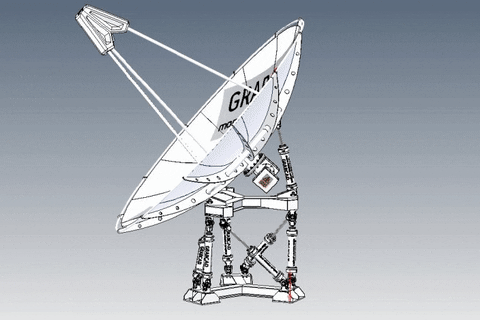
A parabolic antenna is an antenna that uses a parabolic reflector, a curved surface with the cross-sectional shape of a parabola, to direct the radio waves. The most common form is shaped like a dish and is popularly called a dish antenna or parabolic dish. The main advantage of a parabolic antenna is that it has high directivity. It functions similarly to a searchlight or flashlight reflector to direct the radio waves in a narrow beam, or receive radio waves from one particular direction only. Parabolic antennas have some of the highest gains, meaning that they can produce the narrowest beamwidths, of any antenna type.[1][2] In order to achieve narrow beamwidths, the parabolic reflector must be much larger than the wavelength of the radio waves used,[2] so parabolic antennas are used in the high frequency part of the radio spectrum, at UHF and microwave (SHF) frequencies, at which the wavelengths are small enough that conveniently-sized reflectors can be used.
en.wikipedia.org.(2019), Retrieved November 20, 2019, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Parabolic_antenna